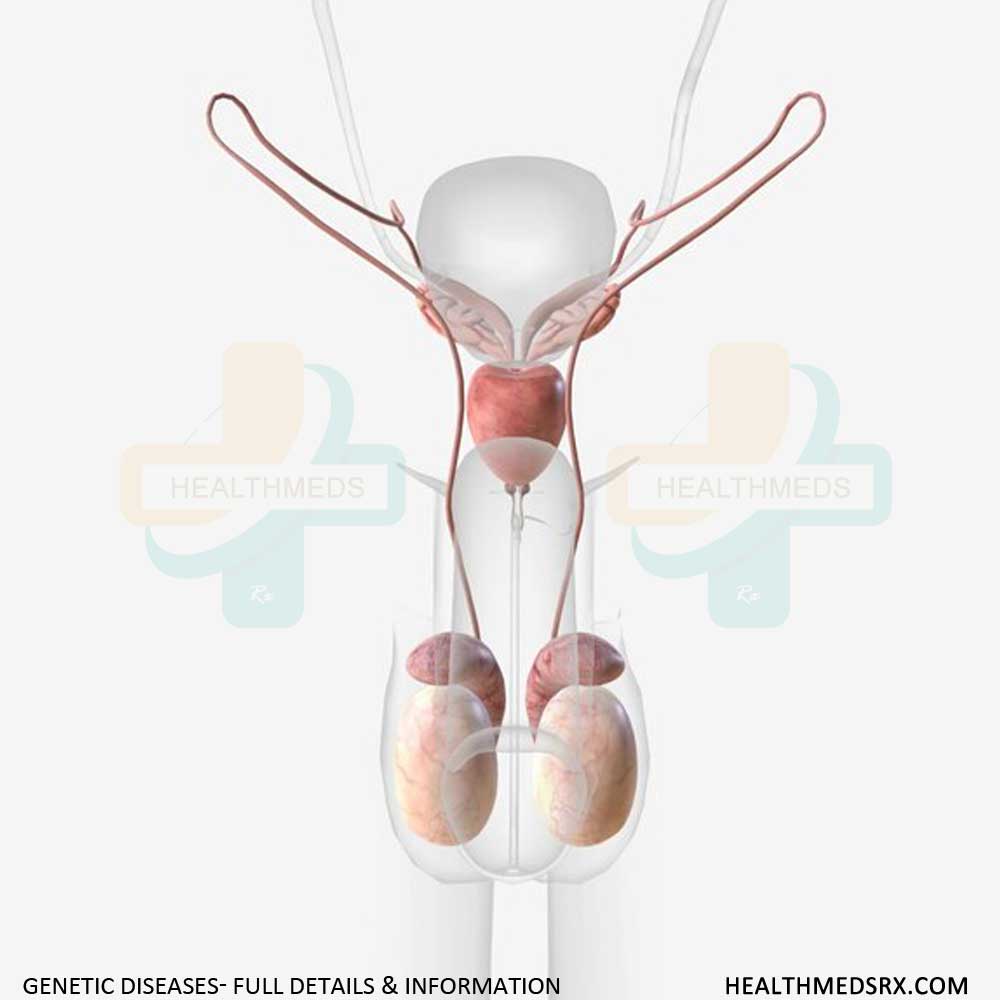
Scrotum is an external part of the male reproductive system. It is located outside the body because it needs to maintain a lower temperature than normal body temperature. Lower temperature supports sperm production. It is surrounded by two oval-shaped glands called testicles. The normal size or thickness is about 8 millimeters (mm).
Scrotum made of smooth sac skin and muscle. It has two layers, one is a parietal layer and another one is a visceral layer. The inner part of the scrotal wall is covered by the parietal layer. Testicles and epididymis coats the visceral layer.
Parts of the scrotum?
The crease called the perineal raphe divides the scrotum into two parts. Appearance of crease like a line down the center. The perineal raphe connects the internal septum with scrotum. Each side contains:
- Testicle: Testicles’ main role is to produce and secrete hormones like testosterone. Tiny tubes and cells called spermatozoa present in the testicles that produce sperm. Once the quality sperms produced in the testicles, it will move to epididymis.
- Epididymis: Epididymis placed at the top of each testicle. The main role of the epididymis is to absorb excess fluid released by testicles to help transfer the sperm through the reproductive tract. It also helps the sperms until they develop into mature condition.
- Spermatic cord: Lymph vessels, nerves and blood vessels present in the Spermatic cords. It also contains a tube called the vas deferens that transfers sperm out of epididymis into ejaculatory ducts.
- Cremaster muscle: Testicles and spermatic cords surrounded by Cremaster muscles. This muscle does an excellent job to keep the testicles under lower temperature for sperm production by avoiding touching the body.
Function of Scrotum
The main role of the Scrotum is surrounding and protecting oval shaped testicles. The scrotal tissues help to guard testicles, blood vessels and other glands. It also acts as a sort of “weather control” system for testicles, because testicles always need a low temperature for good sperm production.
Conditions and Disorders
- Inguinal hernia: A bulge that occurs in the groin region, the area between the lower part of abdomen and thigh. Inguinal hernias occur due to weakening of the muscles in the lower abdomen. Heavy pressure on this area of the body can also be the reason for Inguinal hernias.
- Hydrocele: When a heavy amount of fluid fills up in the scrotum, causing swelling, this condition is called hydrocele. Hydrocele is more common in babies, but sometimes this condition can also happen in adults.
- Varicocele: Enlarged vein or a swollen collection of veins called Varicocele. This type of condition occurs in a man’s scrotum when blood settles in the veins without circulating efficiently out of the scrotum. The main reason for varicocele are Increased hormone activity and standing or sitting in one place for a long time.
- Spermatocele: An abnormal sac or cyst grows on epididymis is called spermatocele. This abnormal cyst does not disappear on its own, but using OTC medications can deal with this issue very easily. Medications can be purchased from Healthmedsrx.com. Commonly very less chance for needing treatment because this cyst doesn’t cause pain or complications.
- Testicular torsion: Testicular torsion happens when a man testicle rotates in his scrotum. Lack of blood supply, nerve function and sperm transport to testicle. This Testicular torsion issue occurs when a man doing heavy physical activity, a minor injury to the testicles or sleep.
- Epididymitis: Inflammation on the coiled tube at the back of testicle is called Epididymitis. This Epididymis carries sperm. Symptoms for this epididymis are swollen, dis-colored or warm scrotum. Commonly men facing testicle pain and tenderness on one side. This epididymitis is easily dealt with by following the medicine treatment.
- Orchitis: Orchitis is the swelling or inflammation of men’s testicles. This orchitis is mainly related to a mumps infection. This Orchitis mainly arises in a man’s life due to bacterial and viral infections. This orchitis is easily dealt with by taking antibiotics with the help of doctor’s advice. But this orchitis is automatically cured by four to six weeks. This issue will cause severe pain in the testicles.
- Testicular cancer: The development of cancer cells in the testicles is called Testicular cancer. This cancer cell spreads from one testicle to another within a few periods.
Common signs or symptoms:
Men can face some symptoms in their scrotum or the area surrounding it, contact healthcare provider immediately:
- Mild or severe pain.
- Swelling, tenderness and redness.
- Rashes or sores.
- Feeling of heaviness.
- Frequent urination.
- Blood in pee or semen.
- Drainage or discharge from penis.
How can men keep scrotum healthy?
Men can keep their scrotum healthy by following these tips:
- Perform a monthly testicular self-exam
- Shower regularly in cold water. Especially scrotum should be chill with cold water.
- Keep the genital area dry after finishing the bath, because sometimes wet scrotum conditions can cause bacterial infections.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing, especially pants.
- Use protection aid while doing sexual intercourse performance. This will avoid several sexual health issues.
- Make use of Erectile Dysfunction medications following proper precautions.
- Avoid shaving hair in the scrotum area. Better to trim the hair scrotum area is good to avoid skin irritation.