Human metapneumovirus (HMPV): Emerging Respiratory Virus in Focus
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) has become a significant respiratory virus affecting millions of people worldwide. This viral infection is a growing concern in public health, especially because it can cause severe respiratory illness in vulnerable populations.
Recent data shows that HMPV infections are becoming more common, with rates reaching all-time highs. The virus is similar to other common respiratory infections, making it difficult to identify without specific tests. It affects people of all ages, but young children and older adults are at higher risk for severe complications.
Key Public Health Implications:
- Rising infection rates demand enhanced surveillance
- Limited testing protocols affect accurate case tracking
- No specific treatments currently available
- Potential strain on healthcare systems during peak seasons
To effectively respond to this public health issue, it is crucial to understand HMPV’s characteristics, how it spreads, and its effects on health. This knowledge will help healthcare providers implement preventive measures and treatment strategies to protect vulnerable populations from severe respiratory complications.
What is HMPV?
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a virus that belongs to the Pneumoviridae family and specifically falls under the Metapneumovirus genus. It is classified as a single-stranded RNA virus. HMPV shares some structural features with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), such as having an envelope and surface proteins that help it enter cells.
Genetic Composition of HMPV
The genetic structure of HMPV consists of:
- A negative-sense RNA genome
- Eight genes that code for important viral proteins
- F and G glycoproteins present on its surface
Evolutionary Origins of HMPV
HMPV has an interesting evolutionary history that connects it to avian metapneumovirus (AMPV), specifically AMPV type C. Scientists believe that HMPV originated from a transmission event where the virus jumped from birds to humans. Over time, it adapted to become a pathogen specific to humans. This relationship between HMPV and AMPV is evident in their genetic similarities, which include:
- 80% sequence identity in multiple viral proteins
- Similar organization of their genomes
- Comparable mechanisms of replication
Genetic Variants of HMPV
The virus exists in two main genetic lineages, known as A and B. Each lineage further contains two sublineages: A1, A2, B1, and B2. These variations play a role in HMPV’s ability to cause repeated infections throughout a person’s life.
History and Discovery of HMPV
In 2001, a team of Dutch researchers at the Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam made an important discovery. Led by Dr. Bernadette van den Hoogen, they identified HMPV while studying unexplained respiratory infections in young children.
How HMPV Was Discovered
The researchers used various methods to identify the virus:
- They analyzed 28 virus samples that had been collected over a 20-year period.
- They employed advanced molecular detection techniques.
- They conducted genetic sequencing to confirm the presence of a previously unknown pathogen.
This discovery generated significant interest in the medical community because it suggested that HMPV had likely been causing respiratory infections for many years without being detected. Further research uncovered stored blood samples from the 1950s that contained HMPV antibodies, providing evidence of the virus’s long-standing presence in human populations.
The identification of HMPV was a major breakthrough in the study of respiratory viruses. It helped explain many cases of respiratory illness, especially in pediatric patients, that had previously lacked a clear cause. As a result of this discovery, diagnostic capabilities improved, and there was a better understanding of respiratory infection patterns in both children and adults. This understanding is crucial as HMPV continues to be a significant cause of respiratory disease worldwide.
Symptoms, Severity, and Demographic Susceptibility of HMPV Infections
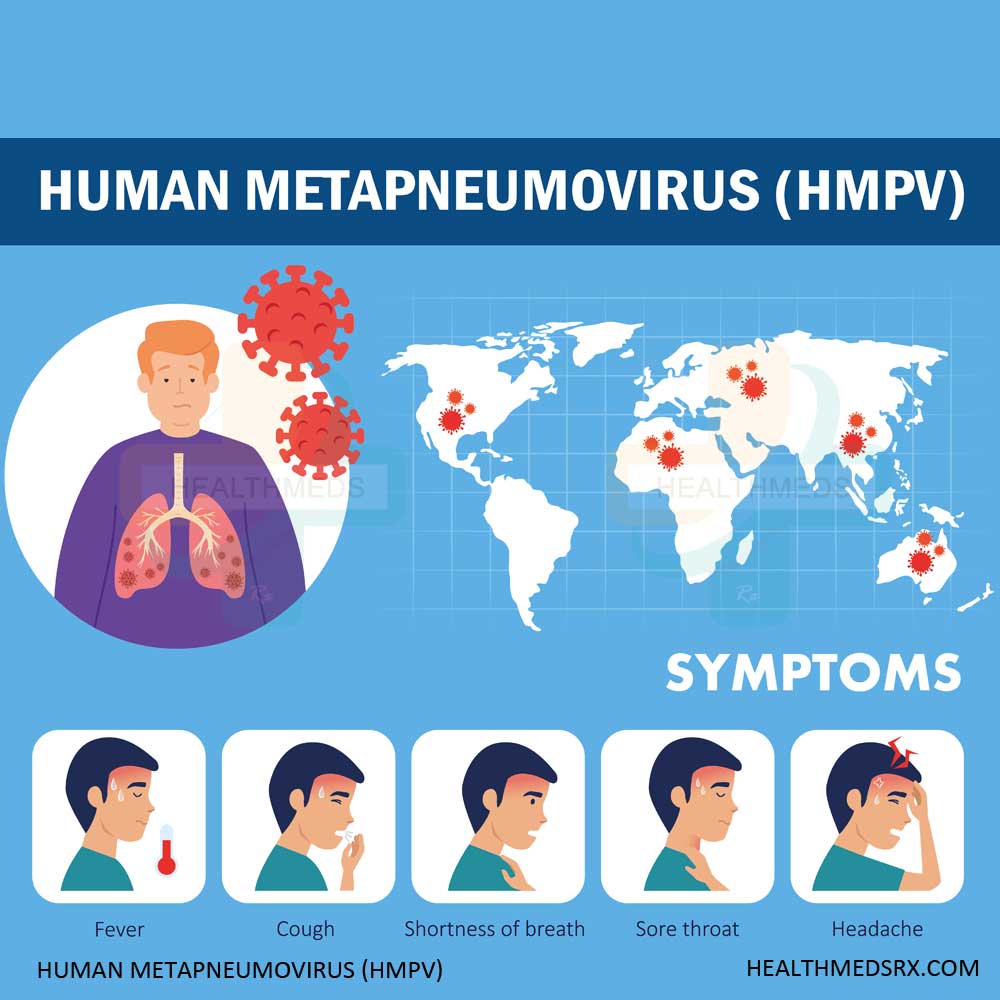
HMPV infections present with symptoms similar to the common cold, ranging from mild to severe manifestations. The primary symptoms include:
- Persistent cough
- Nasal congestion and runny nose
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Body aches
The severity of HMPV infections varies significantly across different age groups. Children under five face the highest risk of developing serious complications, with peak severity occurring between six and twelve months of age. These complications can include:
- Bronchiolitis : Inflammation of small airways
- Pneumonia: Infection of lung tissue
- Severe respiratory distress: Requiring hospitalization
Older adults and individuals with compromised immune systems also face increased risks. Studies show that HMPV can trigger severe respiratory complications in:
- People over 65 years old
- Patients with chronic heart or lung conditions
- Immunocompromised individuals
- Those with asthma or COPD
Reinfections throughout life typically produce milder symptoms due to partial immunity from previous exposures.
Understanding Human metapneumovirus (HMPV): Patterns and Recent Developments
Seasonal Patterns of HMPV Infections
HMPV infections follow distinct seasonal patterns, with peak activity occurring during winter and early spring months. The virus demonstrates a clear preference for colder temperatures, similar to other respiratory pathogens. This aligns with the broader trends observed in acute respiratory infections which often surge during these colder months.
Significant Changes in Human metapneumovirus Infection Rates
Recent surveillance data reveals significant shifts in HMPV infection rates:
- 2023 Surge: A remarkable spike occurred in early 2023, with 11% of tested specimens showing positive results
- Pre-pandemic baseline: Historical data indicates typical positivity rates ranging from 3-7%
- Age distribution patterns: Children under 5 represent 10-12% of all respiratory illnesses caused by HMPV
Geographic Distribution of Human metapneumovirus
The virus exhibits specific geographic distribution patterns:
- Temperate regions experience pronounced seasonal peaks
- Tropical areas show less distinct seasonality but maintain year-round presence
- Urban areas report higher infection rates compared to rural settings
Cyclical Nature of Human metapneumovirus Outbreaks
Research indicates a cyclical pattern in Human metapneumovirus outbreaks, with major peaks occurring every 1-2 years. This pattern suggests viral evolution and population immunity play crucial roles in transmission dynamics. The post-pandemic landscape has witnessed altered seasonal patterns, potentially due to changes in human behavior and interaction patterns. These changes are not only specific to HMPV but also reflect a larger trend observed in the cyclical nature of respiratory infections during the pandemic recovery phase.
Challenges in Diagnosis, Testing, Treatment, and Management Strategies for HMPV Infections
Diagnosing HMPV presents unique challenges in healthcare settings. The primary diagnostic tool, PCR testing, requires specialized laboratory equipment and trained personnel. Many outpatient clinics lack these resources, limiting testing capabilities to hospital environments.
Current Diagnostic Methods:
- Respiratory PCR panels
- Rapid molecular assays
- Viral culture techniques
- Serological testing
The limited availability of Human metapneumovirus testing outside hospitals creates a significant gap in surveillance data. You might experience HMPV symptoms but never receive proper testing, contributing to unreported cases and incomplete epidemiological data.
Treatment Limitations:
- No specific antiviral medications
- Absence of targeted vaccines
- Reliance on supportive care
Healthcare providers manage Human metapneumovirus infections through symptom-based treatments:
- Fever reduction with acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Hydration support
- Rest and monitoring
- Respiratory support in severe cases
High-risk patients, such as immunocompromised individuals or those with chronic respiratory conditions, require careful monitoring and may need hospitalization. The lack of specific treatments emphasizes the importance of prevention strategies and early intervention.
Medical facilities often prioritize testing for other respiratory viruses like influenza or RSV, leaving Human metapneumovirus undetected unless specifically requested. This testing bias affects our understanding of HMPV’s true prevalence and impact on public health.
Research, Future Directions, and Public Health Implications of Human metapneumovirus Infections
Research initiatives targeting Human metapneumovirus have gained momentum in recent years. Scientists at multiple research institutions are exploring potential vaccine candidates through various approaches:
- Live-attenuated vaccines: Researchers modify the virus to create a weakened version that can stimulate immunity without causing disease
- Subunit vaccines: Development focuses on specific viral proteins to trigger immune responses
- Novel delivery platforms: Investigation of innovative methods to enhance vaccine effectiveness
The scientific community has identified several promising research directions:
- Studying cross-protection between Human metapneumovirus strains
- Investigating immune responses in different age groups
- Developing combination vaccines targeting multiple respiratory viruses
Public health systems face significant challenges in addressing HMPV:
- Limited surveillance systems need expansion to track HMPV spread effectively
- Healthcare provider education requires updates on latest Human metapneumovirus developments
- Resource allocation must balance Human metapneumovirus with other respiratory threats
Research teams are working to establish:
- Better diagnostic tools for rapid HMPV detection
- Enhanced surveillance networks to monitor viral mutations
- Improved treatment protocols for vulnerable populations
The integration of HMPV research into broader respiratory virus initiatives has created opportunities for collaborative studies and shared resources. These efforts aim to develop comprehensive approaches to respiratory virus management, particularly focusing on protecting high-risk populations.
The Need for Increased Awareness and Action on HMPV Infections
The rising prevalence of HMPV infections demands immediate attention from the healthcare community and public health sectors. Current data highlights a critical gap in public awareness about this respiratory virus, leaving many at risk of severe complications.
Key priorities for addressing Human metapneumovirus include:
- Implementing targeted public health messaging to educate communities about HMPV symptoms and prevention
- Expanding diagnostic testing capabilities beyond hospital settings
- Developing standardized treatment protocols for healthcare providers
- Supporting research initiatives for vaccine development
Healthcare professionals must recognize Human metapneumovirus as a significant respiratory pathogen requiring vigilant monitoring and proactive management. The path forward requires a coordinated effort between research institutions, healthcare facilities, and public health organizations.
Your understanding of Human metapneumovirus helps protect both individual and community health. Stay informed about HMPV symptoms, seek medical attention when needed, and support initiatives aimed at combating this emerging respiratory threat.

