Behcet’s Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Risk Factors
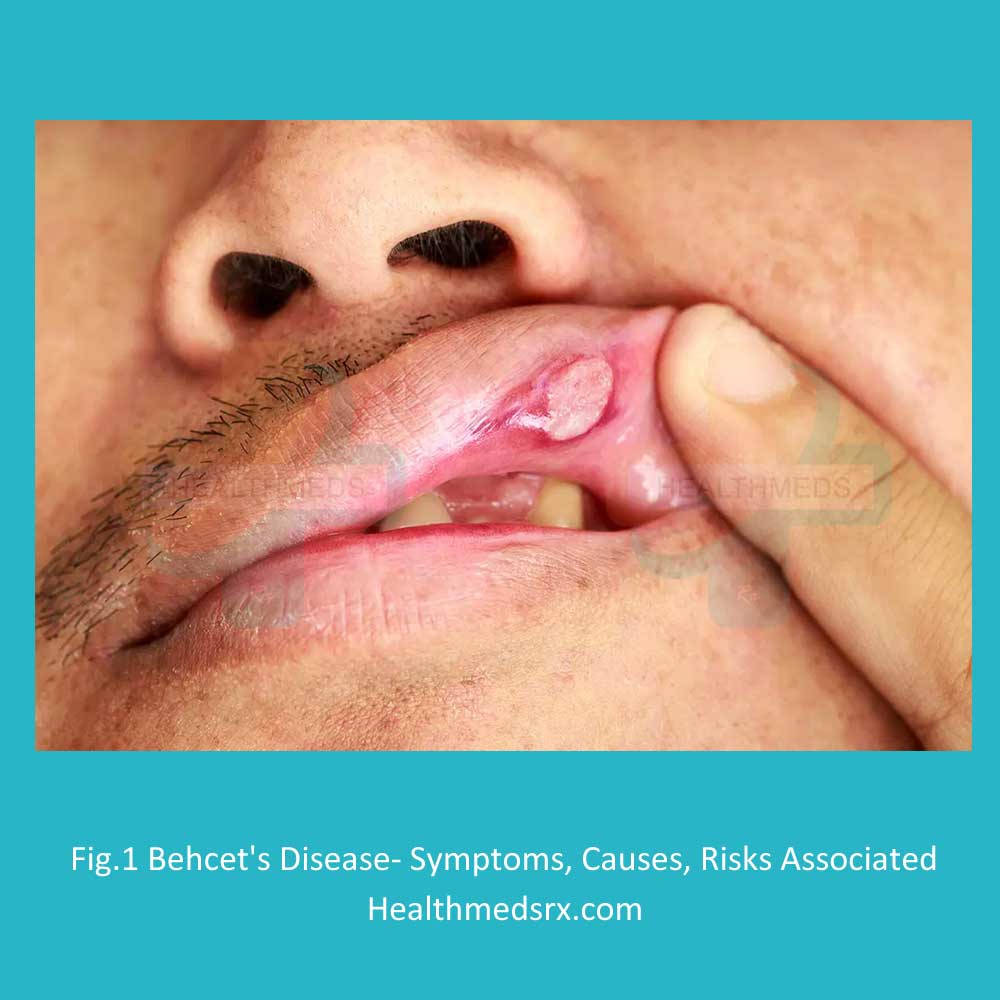
Behcet’s disease is an uncommon autoimmune illness that causes blood vessel inflammation all over the body. Any area of the body can be impacted by this illness. such as eyes, mouth, skin, and joints, etc. Although the specific etiology of Behcet’s disease is unknown, it may be related to genetic factors or an overactive immune system. People with certain genetic origins are more likely to develop the disease.
Its common symptoms include sores on the mouth or genitals, redness around the eyes, and painful joints, which can increase the risk of disability if not treated on time. Treatment for Behcet’s disease focuses on controlling symptoms and reducing flare-ups through lifestyle changes such as avoiding stress and eating a healthy diet, as well as medications designed to reduce inflammation in the affected area.
Blood vessels all across the body become inflamed by Behcet’s illness, a rare autoimmune ailment. Anybody component may be impacted by this illness.
Risk Factors of Behcet’s Disease
The likelihood of developing Behcet’s illness increases for people with specific genetic backgrounds. It is more likely to affect people of Turkish, Korean, Japanese, Iranian, and Arabic ancestry. Behcet’s disease may also be more likely to affect people who have had other autoimmune disorders such as psoriasis or inflammatory bowel disease.
Environmental triggers can increase the risk of developing Behcet’s disease with additional genetic variables. People prone to this disorder manifest more frequently when exposed to certain pathogens. These diseases include the bacteria Epstein-Barr virus, herpes simplex virus, and Streptococcus pyogenes, which cause impetigo and strep throat. Also, smoking is another factor that may increase the risk of developing Behcet’s disease as smokers are three times more likely to develop Behcet’s disease than non-smokers.
Complications of Behcet’s Disease:
Some of the most common side effects of Behçet’s disease are neurological problems, arthritis, and vision loss. The eye is most affected by this disease which can lead to blurred vision and permanent blindness due to inflammation of the cornea or uveitis. Therefore, it is important to treat it on time, in addition, those who have this disease are prone to develop glaucoma or cataracts, which are non-infectious eye diseases.
Behçet’s disease also affects the stomach and intestines, which can cause heartburn, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain due to inflammation of these areas. In addition, those with this condition may also experience polyarthralgia, a type of inflammatory joint pain characterized by frequent joint swelling, stiffness, and other symptoms that can occur as a complication of Behcet’s disease, making it difficult to walk or perform daily activities without discomfort.
Finally, Behcet’s disease patients may experience seizures, tingling in the arms and legs, and headaches brought on by alterations in blood vessels near the brainstem, which may progress to stroke-like symptoms if ignored over an extended period of time.
Treatments for Managing Symptoms
There are several medical treatments available to treat the symptoms of Behcet’s disease. The severity, frequency, and impact of your flare-ups on your daily life will determine the course of treatment. Medical interventions such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants can reduce inflammation in the affected area. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids reduce swelling and pain in the joints, eyes, or other areas affected by Behçet’s disease. And immunosuppressive drugs are effective to control flare-ups; Which suppresses your immune system and helps reduce inflammation.
In addition, biological agents have been developed for use in certain autoimmune disorders such as Behçet’s disease. These drugs target specific immune system components that contribute to inflammatory processes that cause damage throughout the body, relieving symptoms of chronic conditions. Physical therapy is another option for managing mobility issues caused by joint stiffness or discomfort caused by this disorder so that you can easily return to your regular activities.
When choosing a treatment plan for managing your symptoms related to Behcet’s disease, it is important to consider both short-term goals (such as reducing immediate pain) and long-term objectives (like maintaining good vision). It is best to discuss all possible options with your doctor so they can create an individualized plan tailored specifically for you based on factors such as age, lifestyle habits, and current health status among others.
Reducing Symptoms and Managing Behcet’s Disease
Changing your lifestyle can also reduce the symptoms of this disease. there are a few tips you should keep in mind when creating your daily routine like getting plenty of rest, avoiding stressful activities, moderate alcohol consumption, and engaging in regular physical activity such as walking or swimming every day are all recommended ways to help minimize flare-ups associated with this condition.; Eating healthy meals rich in fruits and vegetables that will provide essential nutrients for optimal immune system function; Regularly practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga or mindfulness meditation to manage feelings of anxiety that can trigger episodes if left unchecked. Additionally, seek support from family members or counselors whenever possible so that you don’t feel overwhelmed by any issues that arise from the condition.
Conclusion
By following all the above guidelines individuals with Behcet’s disease can better control their health condition and enable them to live a fuller life despite suffering from chronic illness!

